1.a) Research the following: What are they? How do they work? Refer to examples and explain the benefits.
Communication protocols: worldwide web consortium (W3C); wireless access protocol (WAP); global system for mobile (GSM); 3rd generation protocols (3G); multimedia message service (MMS); general packet radio service (GPRS); Bluetooth; broadband (ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line), cable); voiceover internet protocol (VoIP)
RESEARCH
W3C:
W3C stands for "World Wide Web Constorium." W3C is an international consortium that includes full time staff, industry experts and member organizations. They work together to provide standards for the World Wide Web (www). Their mission is to guide the web to its full potential by developing relevant protocols and guidelines.
By adopting these protocols and guidelines, software and hardware manufacturers can be sure that their programs and equipment will work with the latest Web technologies. W3C was founded by Tim Berners-Lee, who is the inventor of the World Wide Web. Since 1994, when the WWW was created, W3C has played a major role in development of the Web.
WAP:
WAP is short for Wireless Application Protocol, a secure medium that allows you to access information instantly on your handheld devices, such as mobiles phones, radios, smartphones and other communication devices. It is supported by all operating systems, like PalmOS, Windows, FLEXOS, OS/9, JavaOS...
WAP is really good when it comes to dealing with low memory constraints of handheld devices and the low bandwidth constraints of a wireless handheld network. Example site: http://shinewap.mobi/
GSM:
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile communication. GSM is a digital mobile telephony system that is widely used in Europe and other parts of the world. It uses a variation of TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) and it is most used out of three digital telephony technologies (TDMA, GSM and CDMA). It works by compressing the data and then sending it down to a channel with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot. The frequency that it operates is either at 900MHz or 1800Mhz.
3G:
3G is a term used for third generation of mobile phone standards as set by ITU. 3G technologies allow operators to over more service options to their users due to higher communication speed. This allowed operators to give their users mobile broadband and with that came video calls and other services.
UK's 3G providers are: Vodafone, Three, EE and others. With 3G still being used the most used network , 4G is slowly making its way to mainstream with its theoretical speeds going over 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s), while 3G is only capable of only 7.2 Mbps.
MMS:
MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) is a store and forward messaging service that allows its users to exchange multimedia messages with other mobile users. It allows you to send multiple media in one message to multiple recipients including video and audio files. An MMS message will generally cost more than an SMS to send, usually 3 times more than an SMS.
ADSL:
ADSL is an abbreviation of asymmetric digital subscriber line. It basically is a broadband through a telephone line. Unlike dial-up, ADSL can work alongside the frequencies used for telephone calling, allowing you to surf the web without having to block your telephone line. ADSL works with use of Modems and micro filters. It is that these filters split your voice telephone and internet frequencies.
UK's providers are Sky, BT, Talk Talk
VOIP:
VOIP stands for Voice Over Internet Protocol. This technology has became mainstream for the past 9 years, because it offers telephone calls over a broadband internet connection instead of using your regular telephone service. You can connect to a regular telephone line locally or anywhere else in the world, usually for a low price.
How Skype works
First, voice is converted by an Analog Telephone Adapter or IP phone, from an analog signal to a digital one. Then it is sent over the internet in form of data packets. At the arrival it is converted back to an analog signal. By doing this your phone call can be recieved over a traditional telephone worldwide, as well as other VOIP users.
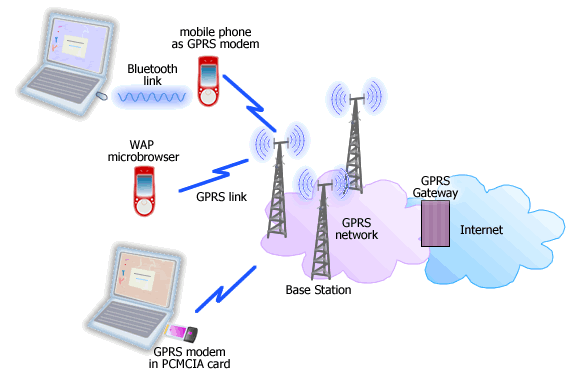
GPRS:
GPRS is short for General Packer Radio Service, a standard in wireless communications that run at speeds of up to 115 Kilobits per second. GPRS also complements Bluetooth, a standard for replacing wired connections between devices with wireless radio connections.
In theory, GPRS services cost less than circuit switched service since communication channels are being userd on a shared-use basis rather than dedicated to only one user at the time.












No comments:
Post a Comment